


Infrared Absorption (IR), is the most common technique in measuring ETCO2. Respiratory, ETCO2 can be a guide for determining the ventilation requirement of a patientĬhanges in respiratory function will affect the removal of CO2 from the lung thus affecting the ETCO2 ETCO2 transport to the lungs is dependent on adequate cardiovascular function any factor that alters cardiovascular function can affect CO2 transport to the lungsĮTCO2 can alert clinicians to changes in the cardiovascular function of the patient with a “normal” respiratory status,Ĭardiac conditions that may decrease ETCO2: hypovolemia, hypotension Early detection of this syndrome is one of the most important reasons for routinely monitoring CO2Ĭirculation, a decrease in ETCO2 is seen with a decrease in cardiac output if ventilation remains constant. The increase occurs early, before the rise in temperature. Malignant hyperthermia is a hypermetabolic state with a massive increase in CO2 production. Metabolic conditions that may decrease ETCO2: hypothermia, paralytics and sedation Metabolic conditions that may increase ETCO2: fever, sepsis, shivering and convulsions Metabolism, changes in ETCO2 can be a reliable indicator in metabolic changes. Therefore, changes in respired CO2 may reflect alterations in metabolism, circulation, respiration, the airway or breathing system. In order for CO2 to be effectively eliminated from the body, there must be adequate blood flow to the lungs, adequate gas exchange across the alveolar-capillary membrane, and adequate ventilation of the lungs to “blow off” the CO2. Once CO2 reaches the lungs, it is eliminated in the process of exhalation.
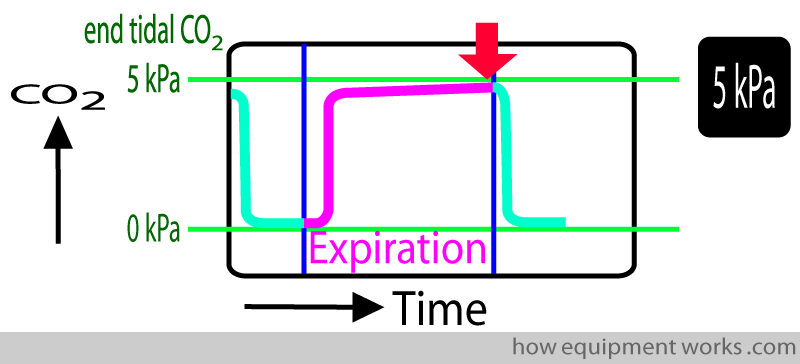
CO2 leaves the cells and is carried by the venous blood to the heart (circulation) and lungs (respiration). If no CO2 is detected this usually indicates the breathing tube is in the oesophagus.Ĭapnography – Measurement of carbon dioxide with a graphic as well as numeric displayĬapnogram – A graphical waveform display of carbon dioxide concentration over timeĬO2 – Carbon Dioxide, a by-product of cellular metabolism that is exhaled during the respiratory cycleĬarbon dioxide (CO2) is a waste product of normal cellular metabolism. Detecting CO2 usually confirms correct placement of the breathing tube in the trachea. It is a requirement of the Association of Anaethetists' recommended "Two-Point Check of Tracheal Tube Placement".Ĭapnographs are connected to the breathing tube in order to detect carbon dioxide, which is only produced by the lungs and isn’t present in the stomach. This is currently the optimal method of continuously monitoring the adequacy of ventilation and circulation in infant, paediatric and adult patients.ĮTCO2 can be of value in the assessment of ventilation, metabolism, and of a patient’s circulation status.Ĭapnography is vital to identify and prevent incidents of unrecognised oesophageal intubation the unintended insertion of a breathing tube into the oesophagus ( the tube which leads to the stomach) instead of the windpipe (trachea). It displays the peak concentration of carbon dioxide occurring at the end of expiration, known as the end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) measurement, either as a partial pressure (in kPa or mmHg) or as a percentage. A Capnograph is a device that measures exhaled carbon dioxide using infrared spectroscopy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
